Tooth decay is a common dental issue that affects people of all ages. It’s not just a matter of aesthetics; it can have serious consequences for your oral health if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what tooth decay is, its symptoms, causes, preventive measures, and treatment options.
What is tooth decay?
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is the result of a gradual breakdown of your tooth’s enamel – the hard, outer layer. This decay occurs when the acids produced by bacteria in your mouth erode the enamel, creating small holes or cavities.
What are the symptoms of tooth decay?

Tooth decay often develops without any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as it progresses, you may experience the following:
- Tooth sensitivity: You might notice discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Toothache: Persistent, throbbing pain in the affected tooth is a common symptom.
- Visible holes or pits: As the decay advances, you may see visible holes or pits in your teeth.
- Bad breath: Foul-smelling breath can be a sign of advanced tooth decay.
- Discolouration: Teeth may appear brown, black, or white-spotted due to enamel erosion.
What are the long-term consequences of untreated tooth decay?
If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to more serious oral health issues, such as:
- Tooth loss: Severe decay may require extraction, resulting in tooth loss.
- Gum disease: Tooth decay can contribute to the development of gum disease.
- Chronic pain: Persistent pain and discomfort can impact your daily life.
- Dental abscess: Infection can spread to the tooth’s root and surrounding tissues, leading to a dental abscess, which is a collection of pus that is formed either inside the teeth, in the gums, or in the bone that holds the teeth in place
Delayed treatment often necessitates more extensive and expensive dental work, so it is highly recommended to consult a dentist when you experience symptoms of tooth decay at its early stages.
What causes tooth decay?
Understanding the causes of tooth decay is crucial for prevention. The primary culprits include:
- Bacteria: Harmful bacteria in your mouth produce acids that attack tooth enamel. These acids, if not properly managed, can erode tooth enamel over time, hence, increasing the risk of tooth decay.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria and food particles. When it lingers on your teeth, it provides an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive and produce damaging acids, which then leads to tooth decay.
- Sugary and acidic foods: Foods and beverages high in sugars and acids directly contribute to tooth decay. Sugars serve as a primary energy source for harmful oral bacteria, while acidic substances can weaken tooth enamel. Overconsumption of these items accelerates decay.

- Dry mouth: Reduced saliva flow can’t effectively neutralise acids. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health. It helps neutralize acids, rinse away food particles, and remineralise tooth enamel. A dry mouth, known as xerostomia, reduces saliva flow, making it harder for your mouth to protect against decay.
Lack of fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that strengthens tooth enamel, making it more resistant to acid attacks. Without sufficient fluoride exposure, enamel becomes more vulnerable to decay, especially in areas with low natural fluoride levels in water.
How do you prevent tooth decay?
Preventing tooth decay starts with good oral hygiene and healthy habits:
- Brush regularly: Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste removes food particles and plaque, preventing the buildup of harmful bacteria and acid-producing substances.
- Floss daily: Flossing reaches the areas between your teeth and along the gumline that your toothbrush can’t access. Removing plaque from these spaces reduces the risk of decay and gum disease.
- Balanced diet: A diet low in sugary and acidic foods and drinks minimises the fuel available to harmful bacteria in your mouth. It also reduces the direct exposure of tooth enamel to acids, preserving its strength.
- Fluoride use: Use fluoride toothpaste and consider fluoride treatments as they strengthen enamel by remineralising it. This added protection makes your teeth less susceptible to acid attacks and decay.
- Regular check-ups: Visit your dentist for regular dental check-up and teeth cleaning. Dental check-ups and cleanings are vital because they allow your dentist to detect and address early signs of decay. Professional cleanings remove stubborn plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing alone can’t eliminate.
- Dental sealants: Sealants are protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars and premolars. They create a barrier that shields these vulnerable areas from the harmful effects of bacteria and acids, making them particularly beneficial for children.
What are the dental treatments for tooth decay?
If tooth decay is detected, your dentist can recommend various treatments, depending on its severity:
- Dental fillings: For minor cavities, your dentist may remove the decayed portion and fill the cavity with a dental filling.
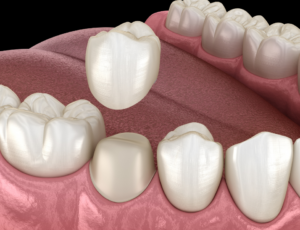
- Dental crowns: Severe decay may require a crown to cover and protect the tooth.
- Root canal treatment: If the pulp of the tooth is infected, a root canal may be necessary to remove the infected tissue.
- Tooth extraction: In extreme cases, a badly damaged tooth may need to be extracted.
Are there any natural remedies for alleviating tooth decay symptoms?
While professional dental care is essential, you can complement it with natural remedies for symptom relief:
How to maintain oral hygiene to prevent tooth decay?
- Oil pulling: Swishing coconut or sesame oil in your mouth can help reduce harmful bacteria.
- Saltwater rinse: Gargling with saltwater can soothe a sore throat and reduce bacteria.
- Xylitol gum: Chewing sugar-free gum with xylitol can promote saliva production and reduce acidity.
How does diet affect tooth decay?
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in preventing tooth decay:
- Calcium-rich foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds strengthen tooth enamel.
- Fruits and vegetables: These high-fiber foods stimulate saliva production, helping to rinse away acids.
- Water: Drinking water, especially fluoridated tap water, helps maintain oral health.
Preserving your smile: The key to beating tooth decay with good dental care
Tooth decay is a prevalent dental issue that can have serious consequences if left untreated. However, with proper oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental check-ups, you can effectively prevent and manage tooth decay. If you have any concerns about your oral health, don’t hesitate to book an appointment with our friendly dental team. Your smile is worth it!
FAQs
What should you expect during a tooth decay evaluation at our dental clinic?
When you visit our clinic for a tooth decay evaluation, our experienced dental professionals will:
- Examine your teeth: Our dentist will visually inspect your teeth and may use X-rays for a closer look.
- Ask about symptoms: Be prepared to discuss any symptoms you’ve experienced.
- Discuss treatment options: If decay is detected, our dentist will discuss appropriate treatment options, which may include fillings, crowns, or root canal therapy.
Can children develop tooth decay?
Yes, children can develop tooth decay. Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is not limited to adults; it can affect individuals of all ages, including children. In fact, tooth decay is one of the most common chronic childhood diseases worldwide.
Several factors contribute to the development of tooth decay in children:
- Dietary habits: Consuming sugary snacks, sweets, and sugary beverages, especially between meals, can increase the risk of tooth decay. Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that attack tooth enamel.
- Inadequate brushing: Children may not have developed proper brushing and flossing habits. Inadequate oral hygiene can lead to plaque buildup on the teeth, which can contribute to tooth decay.
- Lack of fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that helps strengthen tooth enamel and make it more resistant to acid attacks. If children do not use fluoride toothpaste or do not have access to fluoridated water, their teeth may be more susceptible to decay.
- Prolonged use of sippy cups or bottles: Allowing a child to constantly sip on sugary liquids from a bottle or sippy cup, especially at bedtime, can create an ideal environment for tooth decay to develop.
- Infrequent dental visits: Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and prevention of tooth decay. Infrequent dental visits may result in undetected dental problems.
To prevent tooth decay in children, it’s crucial for parents and caregivers to encourage and monitor good oral hygiene practices, limit sugary snacks and drinks, and schedule regular dental check-ups for their children. Early intervention and a focus on prevention can help children maintain healthy teeth and gums as they grow.